Frameworks And Tests in Namshi
As Namshi developers we spend our time doing tickets and coding tasks every day to enhance the website. However these changes are not stable all the time, sometimes some of these new changes end up breaking other working parts of our applications without a prior alert until after we deploy it on our website. As a result we end up having some bugs and hot fixes either immediately after testing the new deployment or later on when people spot the bugs. Therefore Intensive QA is important because the manual test only is not enough, even though if we were careful sometimes we’ll probably forget to test all the affected parts by our changes. And after any deployment we need to test everything and if something was broken we would need to fix is ASAP.
We were working with Zend Framework which is considered as a good framework for MVC projects, but we decided to move to Symfony2 as it is more user-friendly to enhance the structure of our projects and make it more organized, service based applications and most importantly to build automated unit tests. Automated tests are mainly important for testing our tickets and changes before/after they are deployed for quality assurance purposes. Moreover, such tests need to be integrated at early stages because it’s very hard to add them after the development of your application. Therefore, such tests need to be implemented in parallel with your application to make sure you cover all units and aspects of your application.
Testing our project using phpunit
Quality assurance is one of the most important aspects in application development, there are several tests that can be used for web applications like:
Unit Test
Unit Tests are usually conducted to test classes and functions within the application itself. It tests how some functions interact with others and if the desired output and behavior are obtained.
Functional Test
Functional test is mainly used test the integration between our application [Namshi] and other services and layers.
This test is useful for checking how our application functions and interacts with internal and external services.
Why do we waste time on implementing automated tests
If we develop our applications without writing automated tests to save time, we will end up spending more time in fixing issues after each deployment. therefore adding automated tests will save our time, ensure the quality of our application and help us gaining the trust of our customers.
How to implement automated test
With the help of symfony2 implementing automated tests is much easier and feasible. First of all you will need to install phpunit and then develop the test and implement it in your application.
Would automated test modify the application’s data
Automated tests should not affect/modify any data in our application. Therefore we create new databases for the testing environment, then we use data fixtures DoctrineFixturesBundle to insert dummy data into the testing databases, and finally we add/delete required data before/after each test.
Testing Namshi
We are implementing our tests for our application and all the services that interact with it. Our purpose is to cover all aspects of Namshi with automated test (functional test or unit test) to ensure the quality of our application and optimize it.
for now we implemented around 200 test cases

These tests won’t pass if we have any bugs of the application
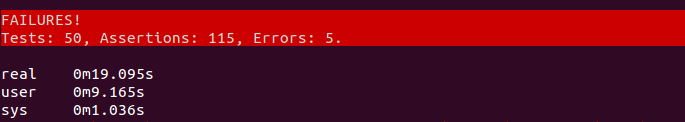
How we assert test results?
we can assert test results in different ways depending on the response that we are expecting:
$this->assertEquals(400, $response->getStatusCode());
$this->assertContains("Expected text", $crawler->filter('*')->text());we can also use DOMXPath to filter html result
$xpath = new DOMXPath($doc);
$this->assertContains('expected value', $xpath->query("//td[@class='html tag class']")->item(0)->nodeValue);or we can expect exceptions
/**
* @expectedException \Namshi\EntityBundle\Exception\InvalidPaymentMethod
*/
public function testServiceWithInvalidPaymentMethod()
{
$data = initial data
$result = $service->execute($data);
}